Nuclear fission is the process of taking a large nucleus and dividing it into smaller nuclei. Commercial power plants and nuclear weapons depend on the fission process. Uranium-235, Uranium-233 and Plutonium-239 undergo fission when struck by a slow moving neutron. A heavy nucleus can split in many different ways. Two different ways that the uranium-235 nucleus splits are shown below:
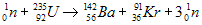
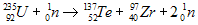
The extra neutrons that are produced by the fission of uranium-235 can then cause additional uranium-235 to go through the fission process. This is called a chain reaction. If the reaction is allowed to proceed unchecked, then a nuclear explosion can result. If the process is moderated or slowed down then the process can be used as a fuel source in a nuclear reactor. In a nuclear reactor, control rods are lowered between fuel rods to slow the fission process by capturing excess neutrons.

